SLAM
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) is a method of generating a map and tracking the robot's location within the map at the same time. It is generally done using laser scan data from a 2D LIDAR and the robot's odometry. For this demo we are using the slam_toolbox package to map our environment. This tutorial will use the Clearpath simulator, but will work on a physical robot too. We will be using a Husky A300 with a Hokuyo UST10 attached to the top of the robot.
See the sample robot.yaml for configuration details.
Make sure you have installed the simulator before starting this tutorial. Take a look at the installation guide for details.
Launching SLAM
When using the simulation, it is important to add use_sim_time:=true to the Nav2, SLAM, and
Localization launch files. When using a physical robot, either omit use_sim_time or set it
to false.
To start SLAM, follow the steps described in the Nav2 startup. When you get to step 4, run
ros2 launch clearpath_nav2_demos slam.launch.py use_sim_time:=true
Building the map
Drive the robot around the world. Ensure you have mapped the region you want the robot to navigate through autonomously.
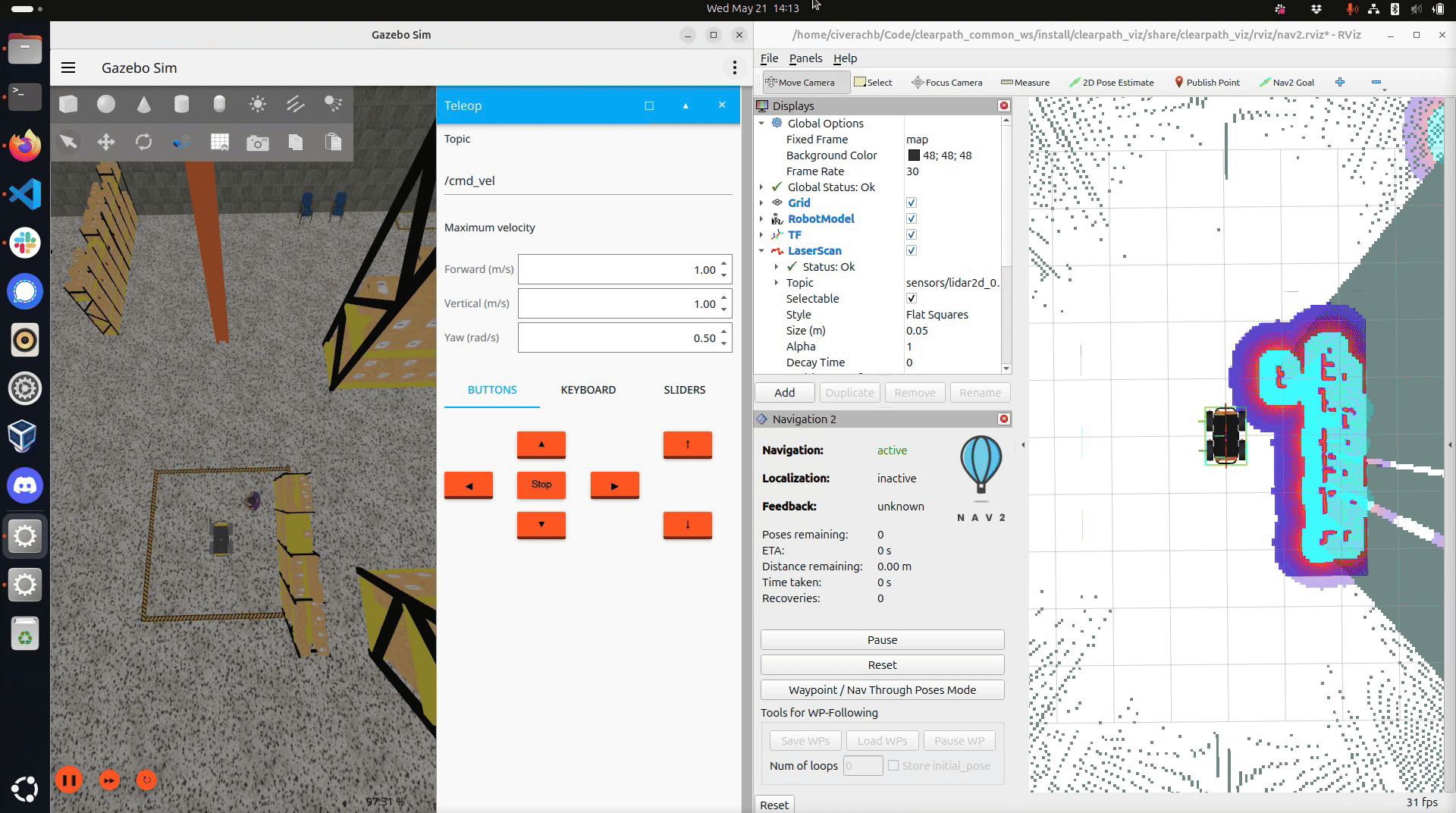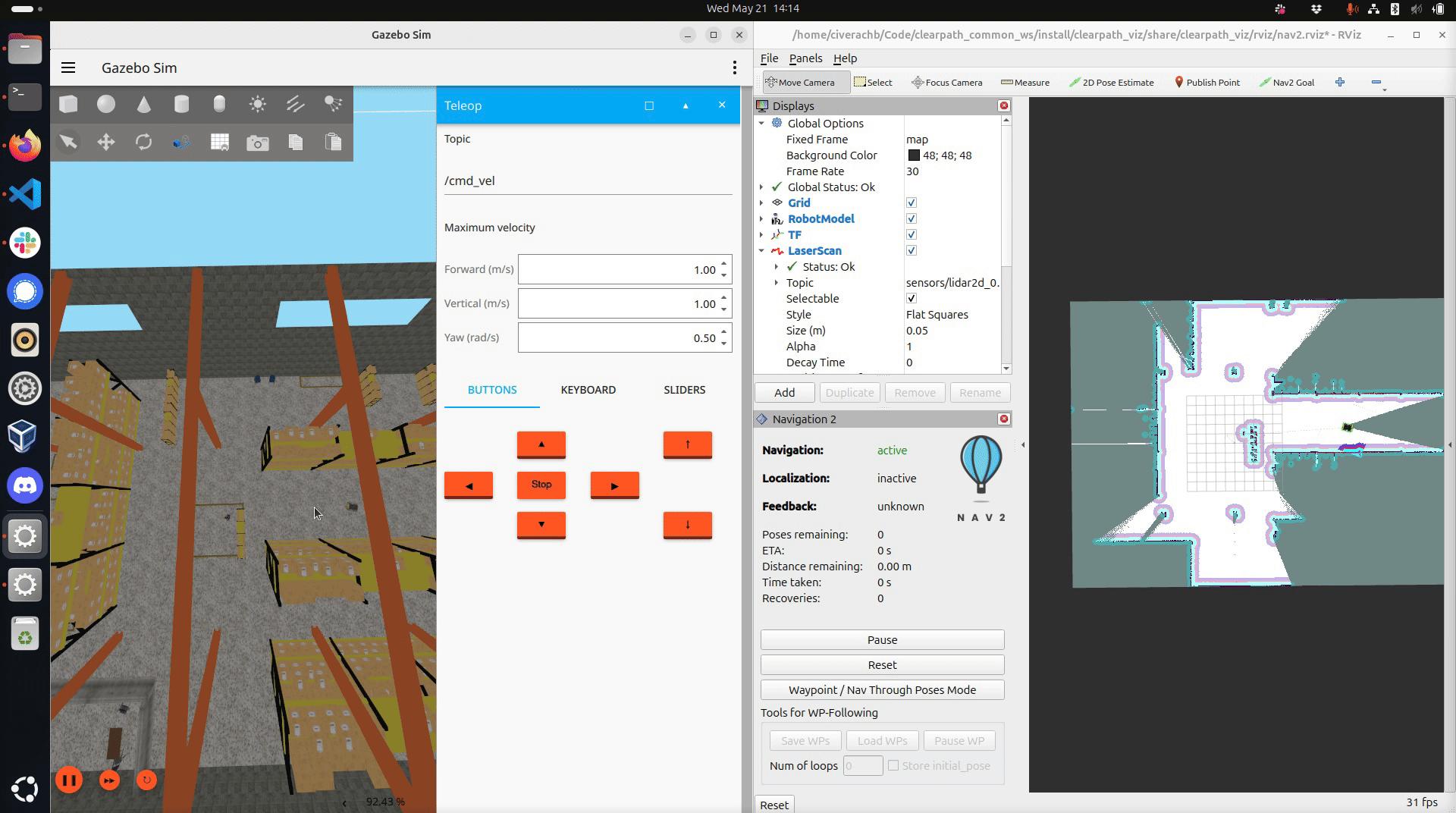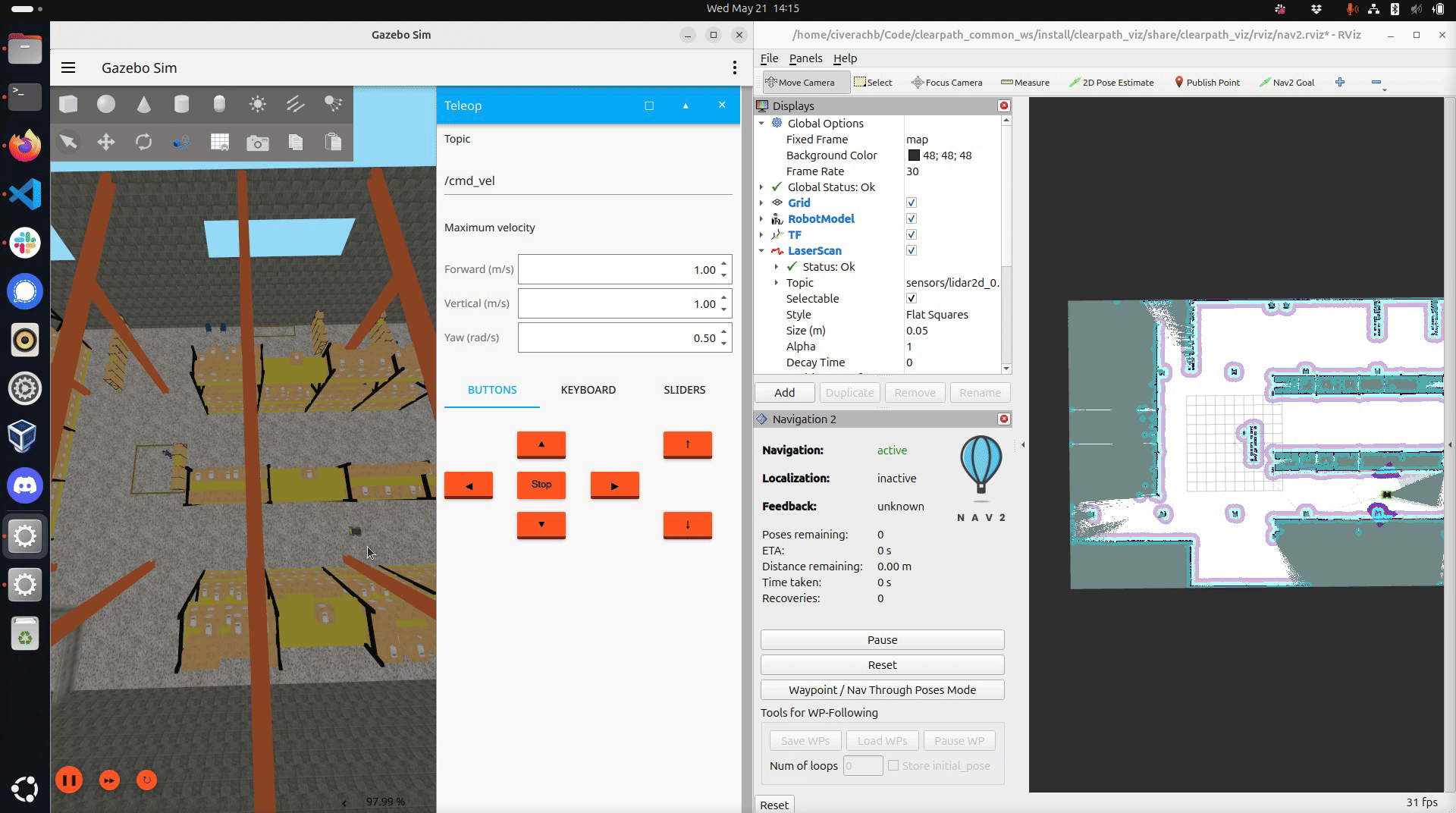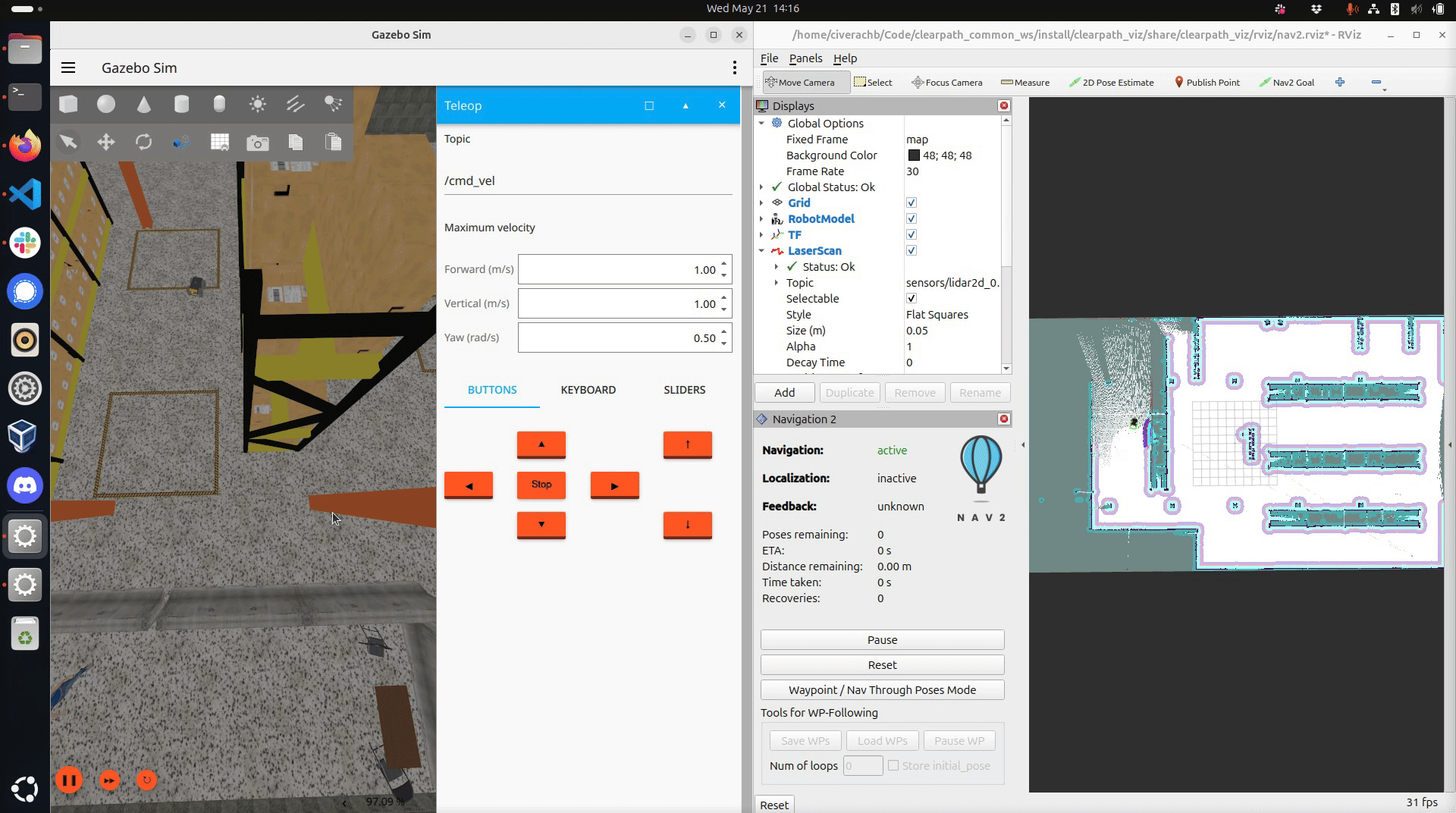
Saving the map
To save the map, open a new terminal and run
ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -f "map_name"
--ros-args -p map_subscribe_transient_local:=true -r __ns:=/a300_0000